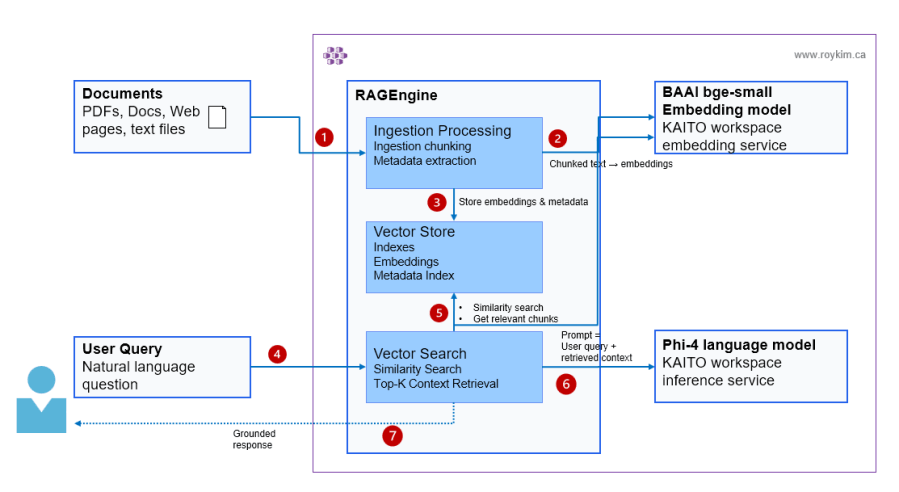
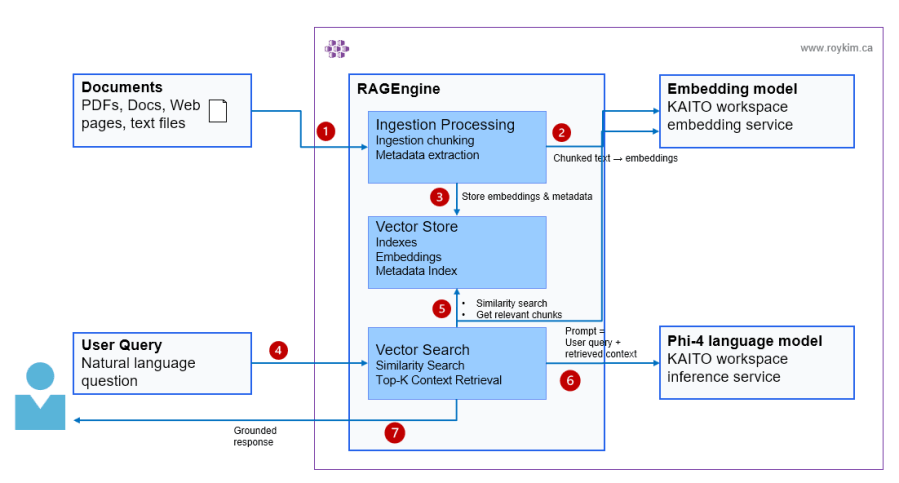
I started by learning how RAG works end-to-end - indexing documents, vectorizing with embeddings, retrieving with hybrid search, and grounding LLM responses. Once I understood the mechanics, I leveled up to Semantic Kernel to introduce agent abstractions and plugin-based extensibility. From there, I explored Azure AI Foundry's hosted agents and prompt engineering patterns. Finally, I built a production multi-agent platform on AKS using the Microsoft Agent Framework SDK, routing five agents across three distinct backends — cloud APIs, on-cluster GPU inference via KAITO, and server-side RAG via KAITO RAGEngine. Each project was a building block toward understanding how enterprise AI applications are designed, orchestrated, and deployed at scale on AKS.