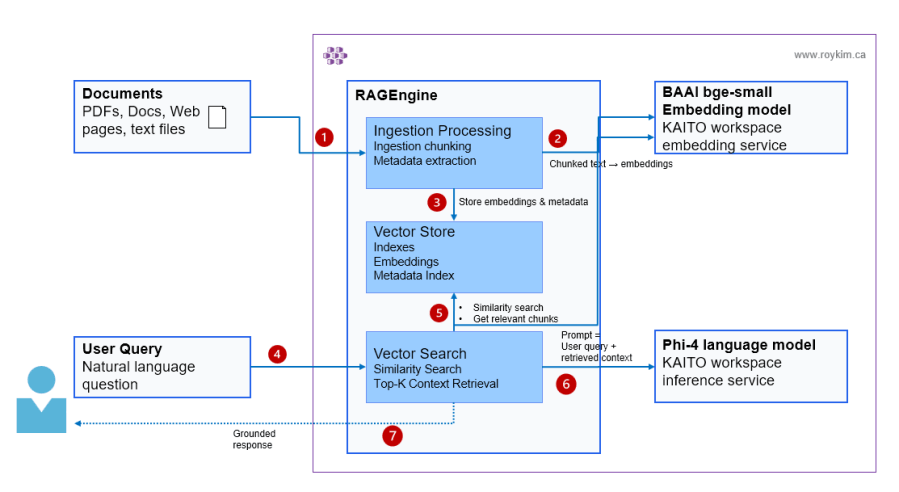
In my previous post I gave an intro and shown my own high level architecture on RAG Engine. I will walk through installing the RAG Engine.
Demo prerequisites (AKS + KAITO Workspace + GPU auto-provisioning)
If you’re following my repo’s flow, the “platform” prerequisites are handled in 1-setup-aks-kaito-v0.80.sh and then 2-setup-nginx-ingress-controller.sh
- Create an AKS cluster
- Install KAITO Workspace Controller
- Install Azure GPU Provisioner (with managed identity + federated credential)
- Deploy an KAITO Workspace (Phi-4) as a model inference service.
The Phi-4 workspace matters because RagEngine needs an inference service endpoint to call. In this repo, the in-cluster URL is shown in 3-setup-kaito-rag.sh as:
http://workspace-phi-4-mini.default.svc.cluster.local/v1/chat/completions
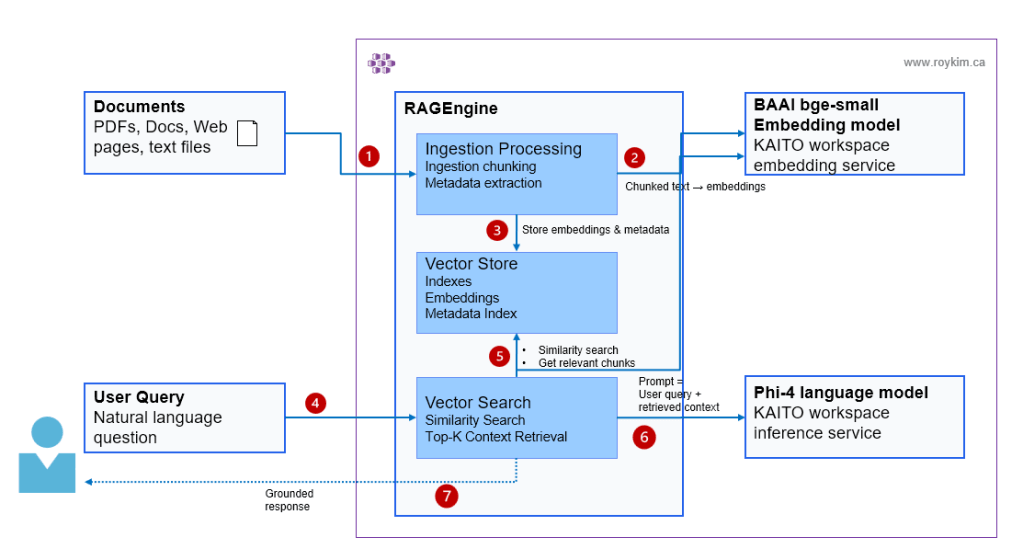
At this point, the AKS node pools have one system node pool, and the other user nodepool with one GPU hosting the Phi-4 model.
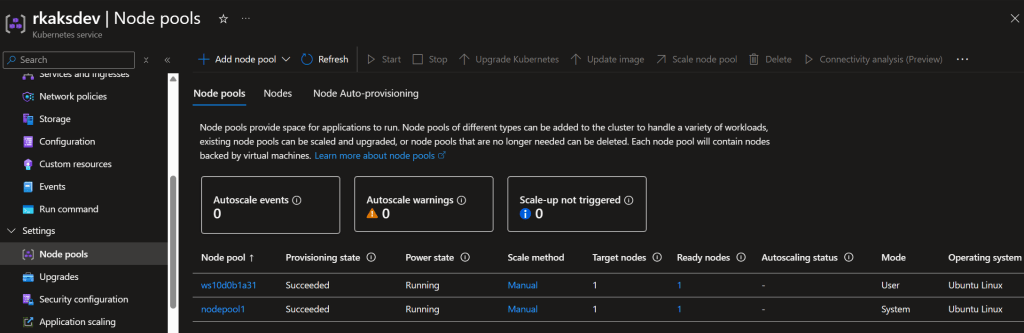
The workspace Phi-4 model inference served as a Kubernetes pod.
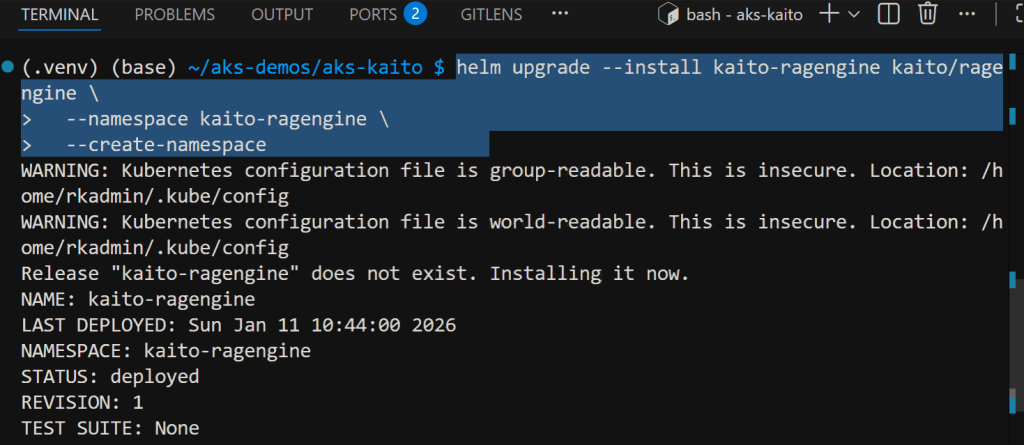
Install RAG engine helm chart
helm repo add kaito https://kaito-project.github.io/kaito/charts/kaito
helm repo update
helm upgrade --install kaito-ragengine kaito/ragengine \
--namespace kaito-ragengine \
--create-namespace
Verify RAGEngine Custom Resource Definition
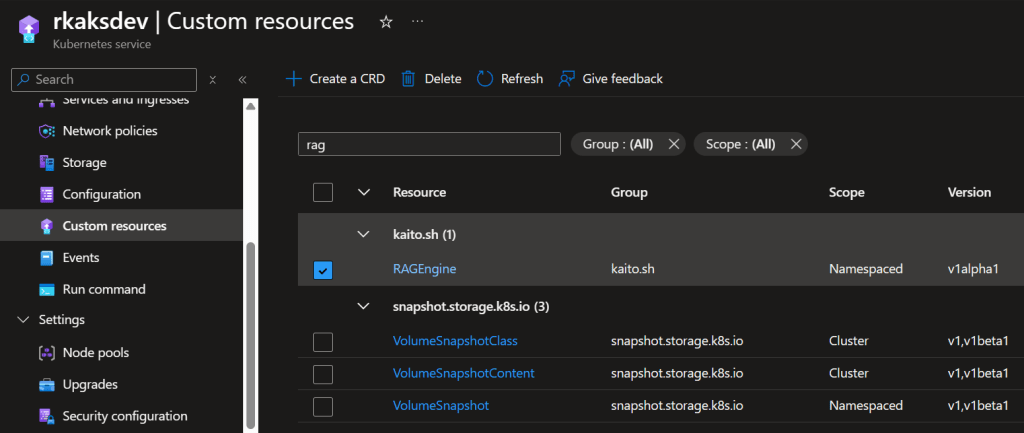
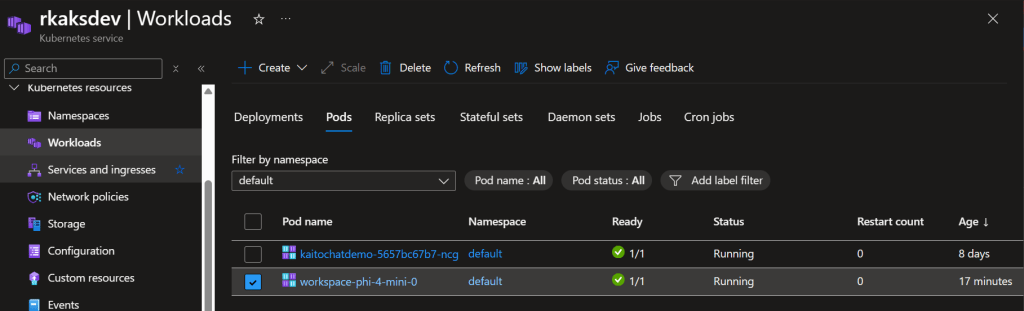
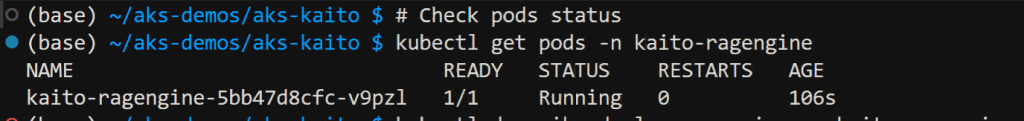
Verify pod status in kaito-ragengine namespace
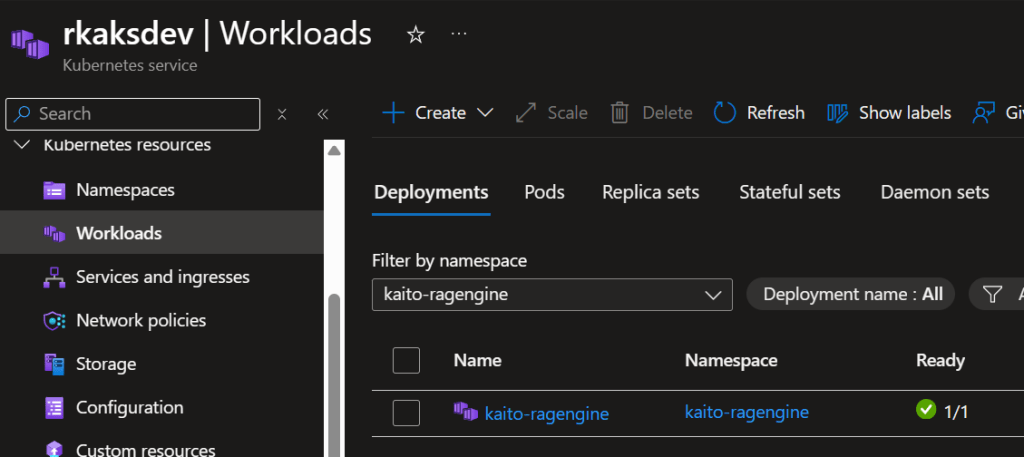
Verify kaito-ragengine workload deployment
Deploy BGE Small RAGEngine that uses the BGE Small model for RAG. This is the k8s yaml manifest
apiVersion: kaito.sh/v1alpha1kind: RAGEnginemetadata: name: ragengine-examplespec: compute: instanceType: "Standard_NC8as_T4_v3" labelSelector: matchLabels: apps: ragengine-example embedding: local: modelID: "BAAI/bge-small-en-v1.5" inferenceService: url: "http://workspace-phi-4-mini.default.svc.cluster.local/v1/chat/completions" contextWindowSize: 4000Apply the manifest.
kubectl apply -f bge-small-ragengine.yaml
As a result the KAITO workspace controller orchestrates the creation of a new nodepool with the VM Sku “Standard_NC8as_T4_v3” supporting a GPU.
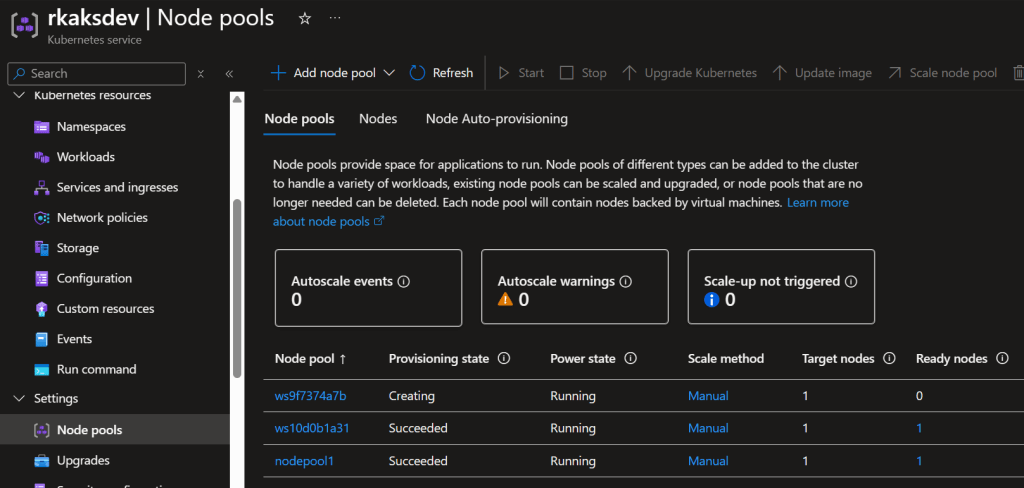
Wait at least several minutes to finish deploying.
RAGengine is deployed and ready.
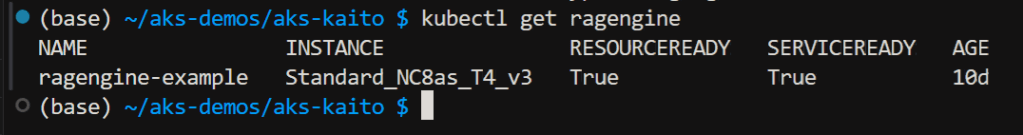
The RAGengine k8s deployment is also deployed.
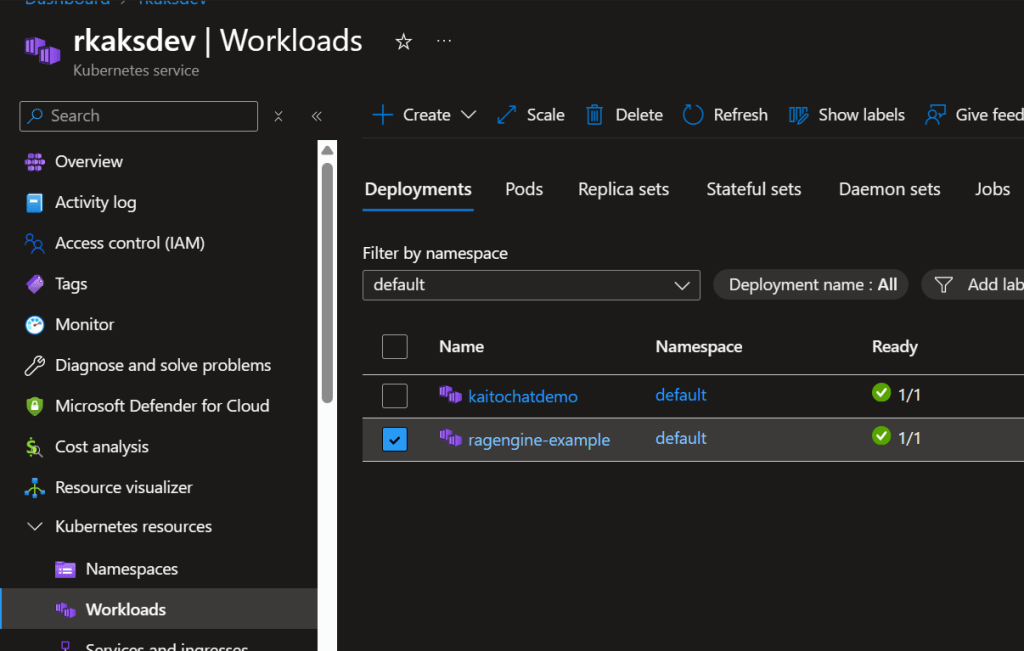
Let’s test the deployed RAG Engine.
First, based on a previously deployed Ingress, get the ingress IP.
INGRESS_IP=$(kubectl get svc ingress-nginx-controller -n ingress-nginx -o jsonpath='{.status.loadBalancer.ingress[0].ip}')I like to setup an ingress controller and ingress rule so I don’t have to do any port forwarding in a local terminal session. See the run book style shell script where I setup the ingress rule for the rag engine at https://github.com/RoyKimYYZ/aks-demos/blob/main/aks-kaito/2-setup-nginx-ingress-controller.sh
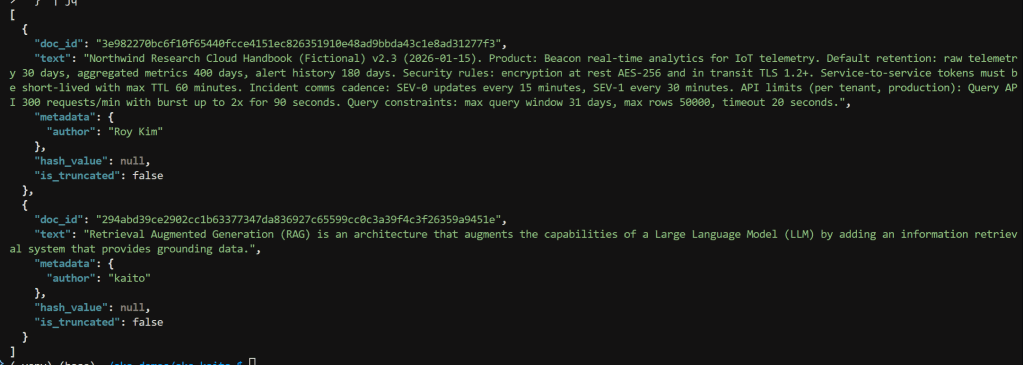
Ingest text documents and create a vector index with the following curl command. There are two documents. The first is some sample text on a fictional cloud handbook
RAG_PATH="rag-nostorage"curl -sS -X POST "http://$INGRESS_IP/$RAG_PATH/index" \ -H "Content-Type: application/json" \ -d '{ "index_name": "rag_index", "documents": [ { "text": "Northwind Research Cloud Handbook (Fictional) v2.3 (2026-01-15). Product: Beacon real-time analytics for IoT telemetry. Default retention: raw telemetry 30 days, aggregated metrics 400 days, alert history 180 days. Security rules: encryption at rest AES-256 and in transit TLS 1.2+. Service-to-service tokens must be short-lived with max TTL 60 minutes. Incident comms cadence: SEV-0 updates every 15 minutes, SEV-1 every 30 minutes. API limits (per tenant, production): Query API 300 requests/min with burst up to 2x for 90 seconds. Query constraints: max query window 31 days, max rows 50000, timeout 20 seconds.", "metadata": { "author": "Roy Kim" } }, { "text": "Retrieval Augmented Generation (RAG) is an architecture that augments the capabilities of a Large Language Model (LLM) by adding an information retrieval system that provides grounding data.", "metadata": { "author": "kaito" } } ] }' | jqThe JSON response indicates doc_id of the text chunk, the text chunk along with assigned metadata.
To list indexes, run the curl command
curl -sS "http://$INGRESS_IP/$RAG_PATH/indexes" | jq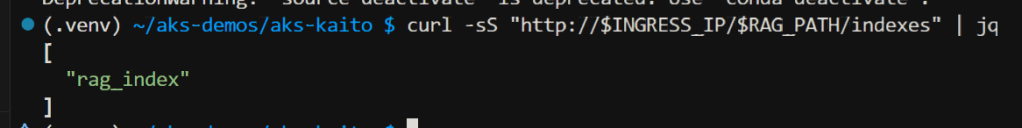
Now to ask a question against the indexed documents via RAG Engine, “What is the default retention for raw telemetry vs aggregated metrics vs alert history? Give the numbers and units.“
I run the following curl command.
model=phi-4-mini-instruct
curl -sS -X POST "http://$INGRESS_IP/$RAG_PATH/v1/chat/completions" \
-H "Content-Type: application/json" \
-d '{
"index_name": "rag_index",
"model": "phi-4-mini-instruct",
"messages": [
{"role": "system", "content": "You are a knowledgeable assistant."},
{"role": "user", "content": "What is the default retention for raw telemetry vs aggregated metrics vs alert history? Give the numbers and units."}
],
"temperature": 0.5,
"max_tokens": 2048,
"context_token_ratio": 0.5
}' | jq
The JSON response consists of the content field with value
“Raw telemetry: 30 days
Aggregated metrics: 400 days
Alert history: 180 days”
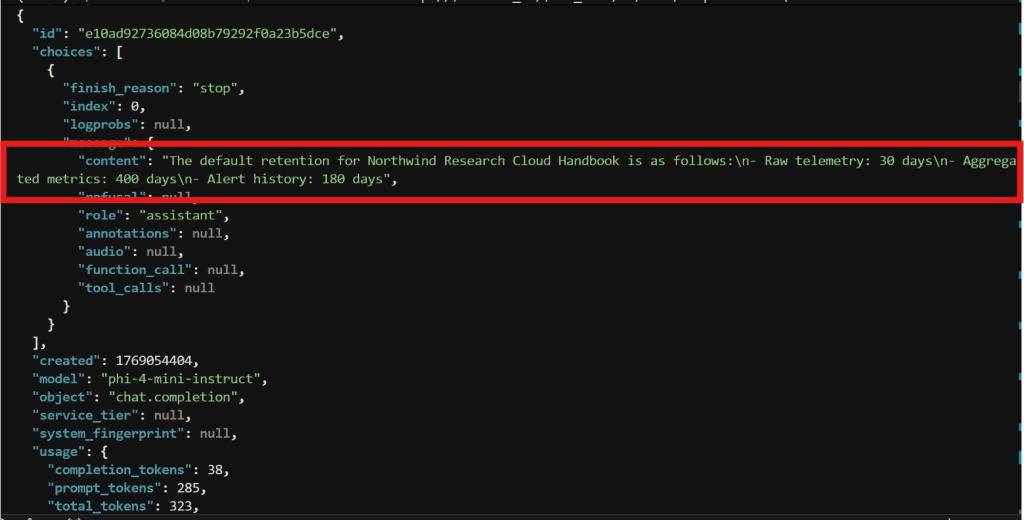
The response is “The default retention according to the Northwind Research Cloud Handbook v2.3 is as follows:\n\n- Raw telemetry: 30 days\n- Aggregated metrics: 400 days\n- Alert history: 180 days”
Note that the curl command against the chat completion API is set with the model as phi-4-mini-instruct. This model is used to take the search result(s) and provide a grounded response back to the user.
Final Thoughts
I have shown an option to implement a RAG solution that you can manage and control all in your AKS cluster. Also there is less plumbing involved to build a RAG solution but with KAITO RagEngine you get some of it out-of-the-box.
Pingback: Doc Ingestion CLI for AKS KAITO RAG Engine – Roy Kim on Azure and AI